A COMPREHENSIVE QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE EVALUATION OF EXTRAPOLATION OF INTRAVENOUS PHARMACOKINETIC PARAMETERS FROM RAT, DOG, AND MONKEY TO HUMANS. I. CLEARANCE
$ 7.50 · 4.6 (445) · In stock

This study was conducted to comprehensively survey the available literature on intravenous pharmacokinetic parameters in the rat, dog, monkey, and human, and to compare common methods for extrapolation of clearance, to identify the most appropriate species to use in pharmacokinetic lead optimization, and to ascertain whether adequate prospective measures of predictive success are currently available. One hundred three nonpeptide xenobiotics were identified with intravenous pharmacokinetic data in rat, dog, monkey, and human; both body weight- and hepatic blood flow-based methods were used for scaling of clearance. Allometric scaling approaches, particularly those using data from only two of the preclinical species, were less successful at predicting human clearance than methods based on clearance as a set fraction of liver blood flow from an individual species. Furthermore, commonly used prospective measures of allometric scaling success, including correlation coefficient and allometric exponent, failed to discriminate between successful and failed allometric predictions. In all instances, the monkey tended to provide the most qualitatively and quantitatively accurate predictions of human clearance and also afforded the least biased predictions compared with other species. Additionally, the availability of data from both common nonrodent species (dog and monkey) did not ensure enhanced predictive quality compared with having only monkey data. The observations in this investigation have major implications for pharmacokinetic lead optimization and for prediction of human clearance from in vivo preclinical data and support the continued use of nonhuman primates in preclinical pharmacokinetics.

PDF] A comprehensive quantitative and qualitative evaluation of extrapolation of intravenous pharmacokinetic parameters from rat, dog, and monkey to humans. I. Clearance.
Pre-Clinical Pharmacokinetics, Tissue Distribution and Physicochemical Studies of CLBQ14, a Novel Methionine Aminopeptidase Inhibitor for the Treatment of Infectious Diseases. - Document - Gale OneFile: Health and Medicine
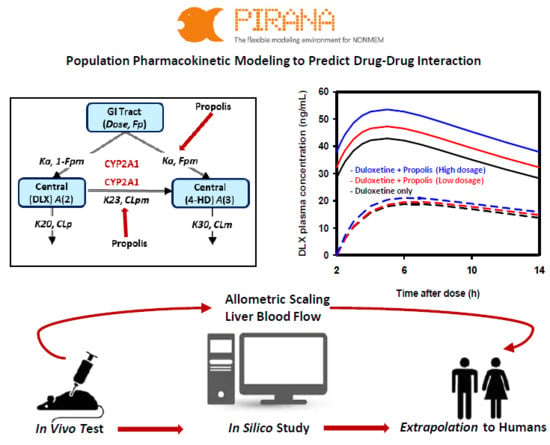
IJMS, Free Full-Text

Adenovirus Capsid-Based Anti-Cocaine Vaccine Prevents Cocaine from Binding to the Nonhuman Primate CNS Dopamine Transporter

IJMS, Free Full-Text
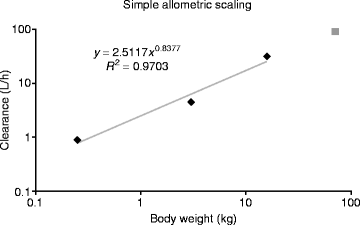
Dose Finding in Single Dose Studies by Allometric Scaling

Extrapolation of human pharmacokinetic parameters from rat, dog, and monkey data: Molecular properties associated with extrapolative success or failure - ScienceDirect
Pre-Clinical Pharmacokinetics, Tissue Distribution and Physicochemical Studies of CLBQ14, a Novel Methionine Aminopeptidase Inhibitor for the Treatment of Infectious Diseases. - Document - Gale OneFile: Health and Medicine

Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Modeling of the Bisphenols BPA, BPS, BPF, and BPAF with New Experimental Metabolic Parameters: Comparing the Pharmacokinetic Behavior of BPA with Its Substitutes, Environmental Health Perspectives

Quantitative Assessment of Blood Lactate in Shock: Measure of Hypoxia or Beneficial Energy Source

In Silico Categorization of in Vivo Intrinsic Clearance Using Machine Learning

Candidate Translational Characterization