Muscle Regeneration
$ 12.99 · 4.8 (184) · In stock

Fibroadipogenic progenitors (FAPs) and skeletal muscle regeneration Skeletal muscles are capable of regenerating after damage. This is possible owing not only to myogenic stem cells (MSCs), from which new myofibers originate, but also to several non-myogenic cell types resident in muscles. Among these, fibro-adipogenic progenitors (FAPs) are known progenitors of tissue-fibroblasts/myofibroblasts and adipocytes. FAPs, are…

Exercise enhances skeletal muscle regeneration by promoting senescence in fibro-adipogenic progenitors

PDF] Mechanisms Regulating Muscle Regeneration: Insights into the Interrelated and Time-Dependent Phases of Tissue Healing
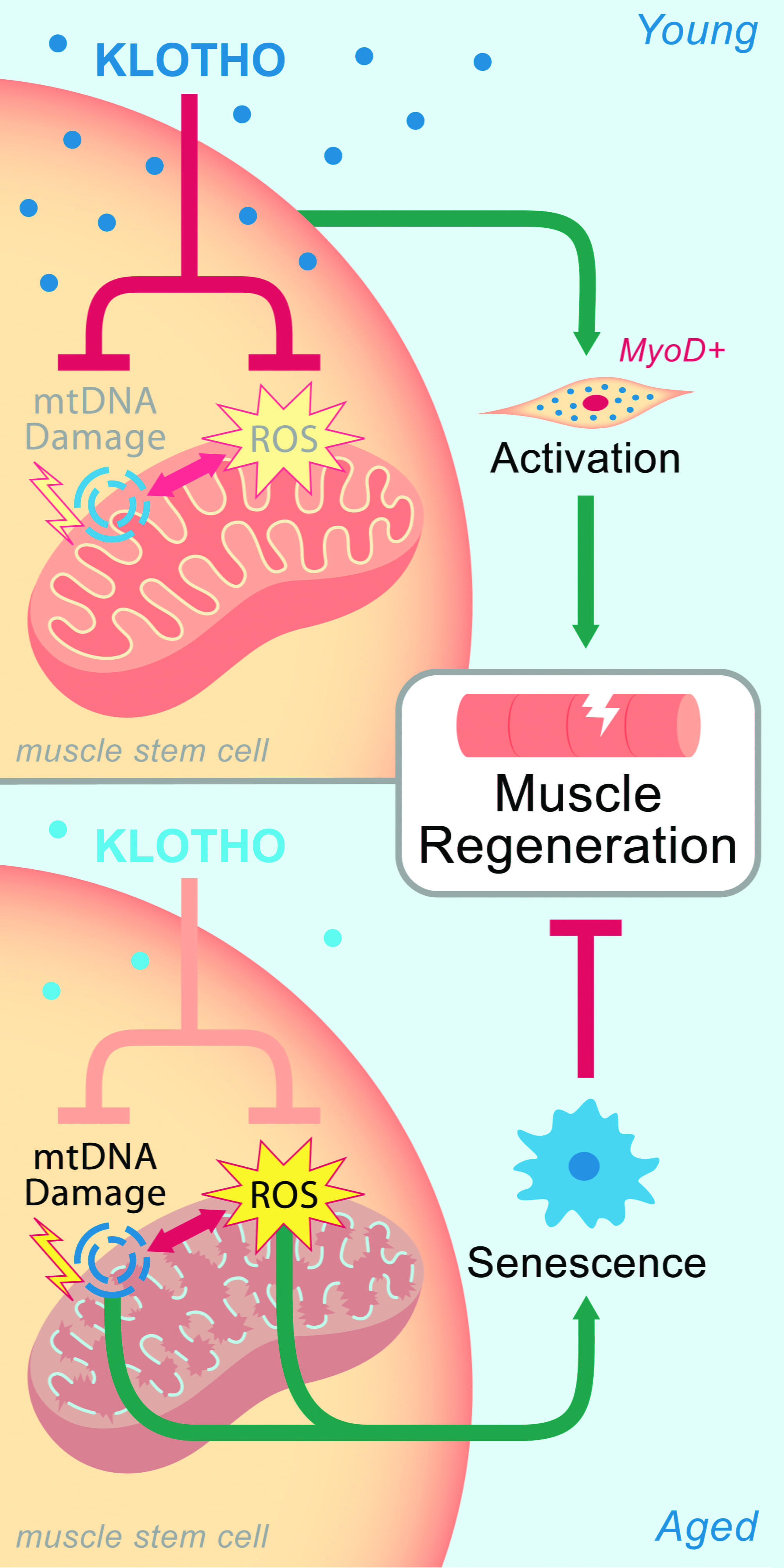
Longevity Protein' Rejuvenates Muscle Healing in Old Mice

Therapeutic Sources of Skeletal Muscle Regeneration from Volumetric Muscle Loss: A Narrative Review
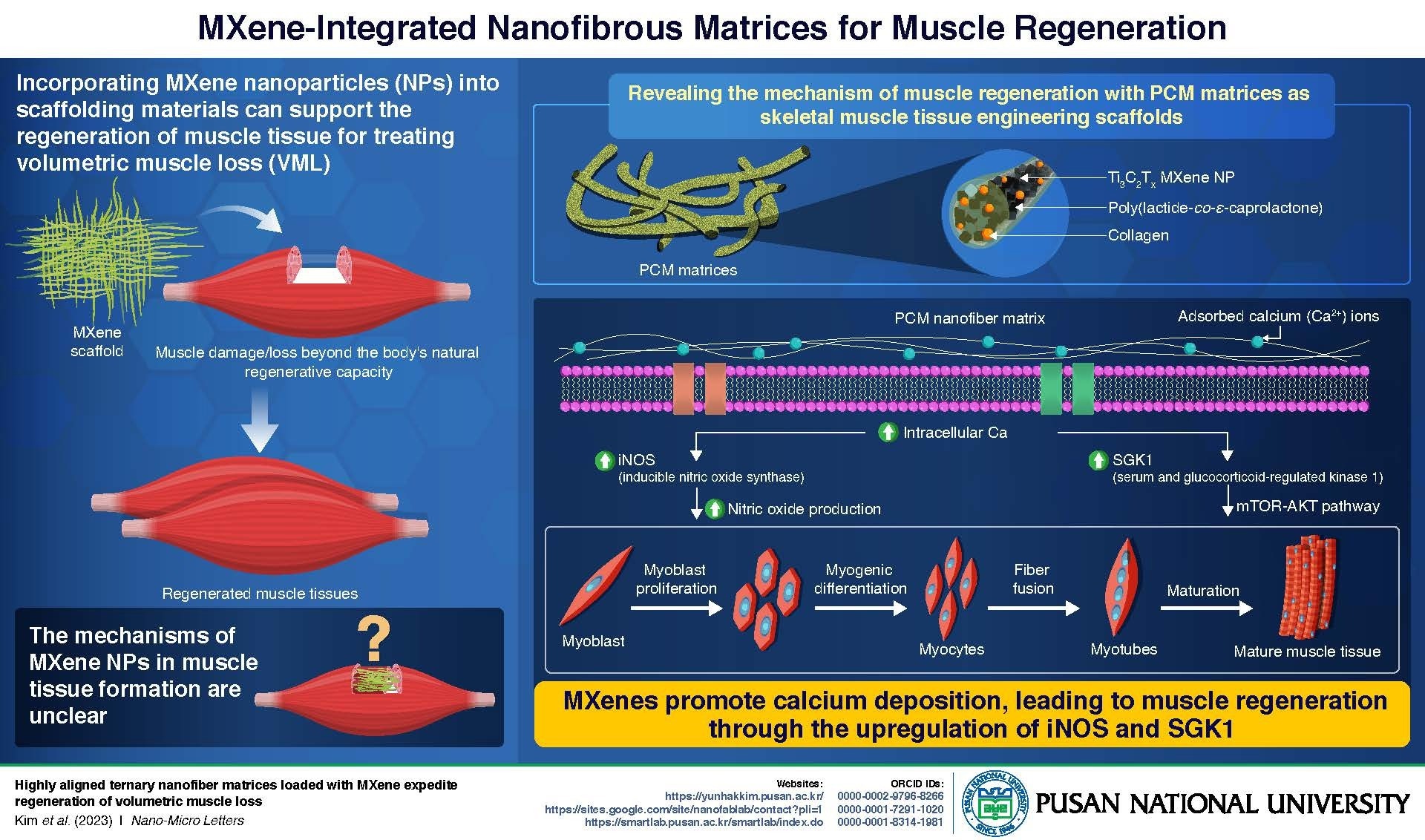
Pusan National University's Breakthrough in Muscle Regeneration: Nanotech Scaffolding Supports Tissue Growth

Regenerating motor neurons prime muscle stem cells for myogenesis by enhancing protein synthesis and mitochondrial bioenergetics

New strategy to facilitate muscle regeneration after injury

Muscle Regeneration

JCI - IRE1α regulates skeletal muscle regeneration through myostatin mRNA decay

JCI - IRE1α regulates skeletal muscle regeneration through myostatin mRNA decay

Skeletal Muscle Satellite Cells and Macrophages Regulate Skeletal Muscle Regeneration - AcceGen

Age-dependent alteration in muscle regeneration: the critical role of tissue niche