trigonometry - Why is the cosine of a right angle, 90 degrees, equal to zero? - Mathematics Stack Exchange
$ 22.99 · 4.6 (492) · In stock

Why the cosine of an angle of 90 degree is equal to zero? By definition we know that: $$\text{cos } \alpha = \frac{\text{adjacent}}{\text{hypotenuse}}.$$ If we want to apply the definition to the

trigonometry - Prove that the cosine distance between any two vectors of 0's and 1's of the same length is at most 90 degrees. - Mathematics Stack Exchange

Trigonometry SpringerLink

Time Shifting Properties of Fractional Differencing, by NTTP
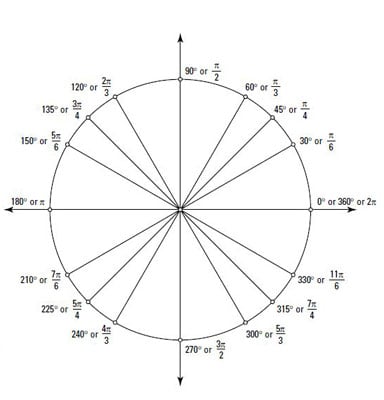
Positive and Negative Angles on a Unit Circle - dummies
Let a force with two equal components each of magnitude F. What is the magnitude of force? I know that answer is √2/F but need an explanation. - Quora
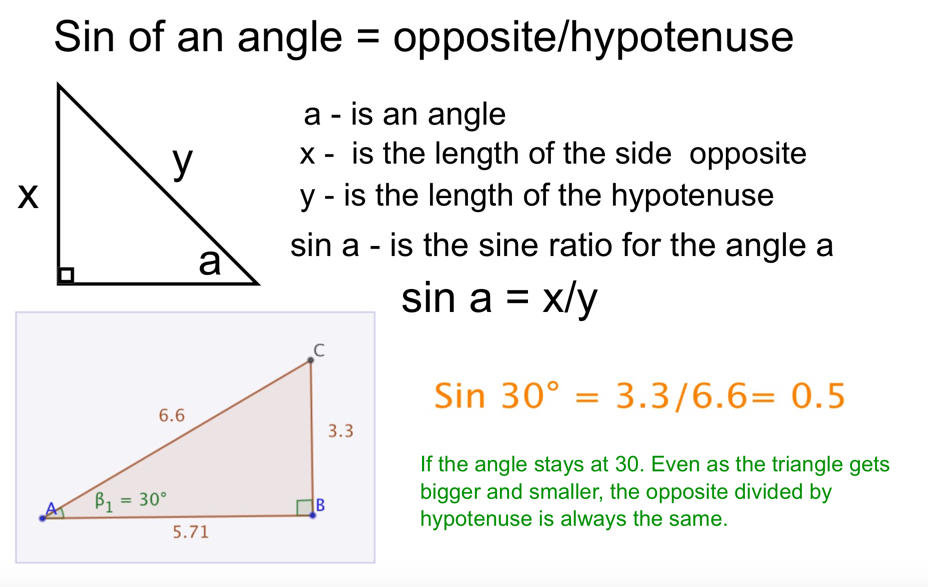
Right angled Trigonometry
How to find values of non-standard angles like 46, 55, 98, 102 degrees in trigonometry without the help of a calculator and log book as both are not used in the exam - Quora
Could a cosine wave be considered a 90 degrees out of phase of a sine wave, if it isn't mentioned that its cos wave? - Quora
Sine and cosine - Wikipedia

geometry - Trouble with Proof of Sine Sum Formula - Mathematics Stack Exchange
Trigonometry and Cosine similarity

trigonometry - Why are the Trig functions defined by the counterclockwise path of a circle? - Mathematics Stack Exchange
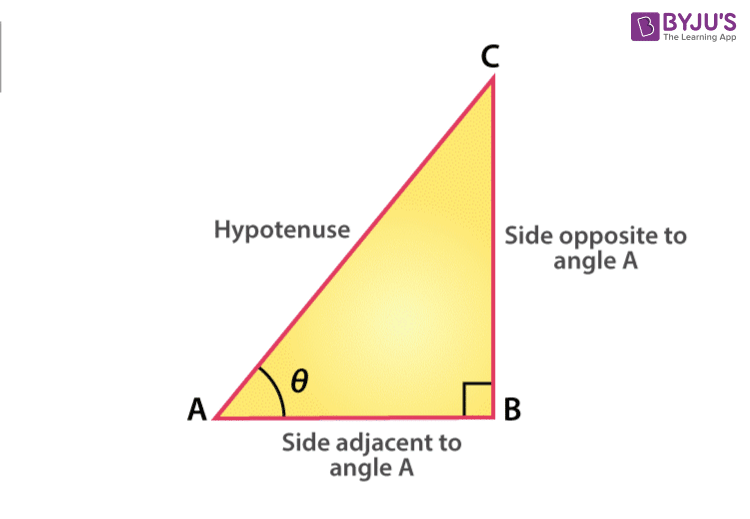
Sin 90 Degrees I Formula and its Derivation I Sample Examples

Time Shifting Properties of Fractional Differencing, by NTTP
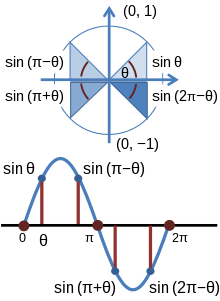
Trigonometric functions - Wikipedia

